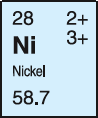
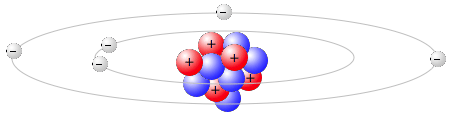
|
| Home - Return to Unit 2 Resources |
- Welcome to another BC Science 10 practice quiz!
- Pick the best answer for each question.
- Your score will decrease with every wrong guess. If you guess wrong 3 times on a question, you will receive no points.
- Get every answer correct the first time to score 100%. Good luck!
- If you wish to try the quiz again, just click the "reload" button in your browser.